Everything You Need To Know About Personal Protective Equipment

Regardless of the industry where you are employed, there is an expectation of a safe and healthy workplace. While there are a variety of hazards that could be present in any given environment, safety precautions involve having the right personal protective equipment to reduce the risk of harm or injury to the body. It isn’t always feasible to have physical protective structures in the work environment, leading to the need for distribution of protective gear to employees or those who are at potential risk.
There are several different types of safety gear, and there are specific situations or circumstances which dictate which use is most appropriate. Training and proper use are also important for ensuring PPE is an effective safety measure. Here you will find the information needed to make sure your use of protective equipment is effective and right for a safety situation.
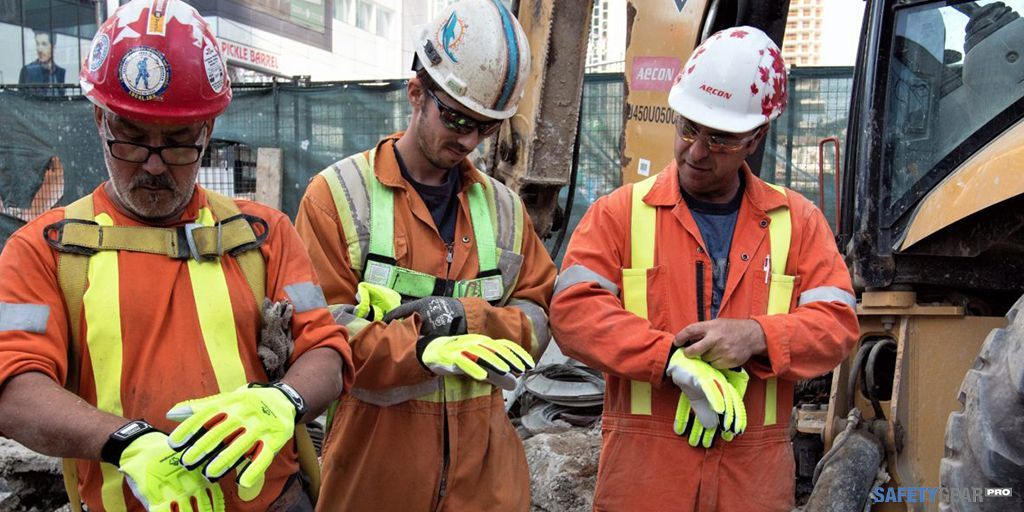


Ensuring Proper Use
There are requirements for the use of protective equipment, as outlined by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration. OSHA guidelines also establish what equipment must be used for protection in the different categories of exposure. An employer may also be required to issue the necessary safety equipment to employees at the company’s expense, with all but a few exceptions to this OSHA regulation.
Ensuring Proper Construction
The goal of protective equipment to reduce the likelihood of an individual suffering an injury during an accident while at work. Any items used must have the highest quality in both design and construction, and it should be of an appropriate fit for the individual wearing it. Many of the categories of equipment have design standards that have been set by the American National Standards Institute, an agency known for its leadership role in establishing safety standards with U.S. workers since the 1920s. Whether employer-provided or employee purchased, all personal protective equipment should be in compliance with all ANSI standards.
Ensuring Proper Coverage
There are several different categories of protective equipment, each focusing on protecting a different area of the body. Not all categories are necessary for each job or employee, but those who require them for their job duties should be trained in the appropriate way to wear, clean, and store the equipment.
Eye & Face Protection
Employees whose faces and eyes are exposed to hazards must be outfitted with certain elements of eye and face protection. Occupations eye injuries can occur because of physical trauma to the eyes, as well as particle damage from acidic liquids, chemical vapors or liquids, molten metal, or harmful light radiation. Prescription lenses aren’t a reliable form of protection, so safety glasses with a prescription or glasses that can be worn over prescription lenses are required. Those working as carpenters, machinists, electricians, welders, laborers, assemblers, or other manual labor positions should be outfitted with eye and face protection. Goggles, safety glasses, welding shields, or face shields are appropriate.
Head Protection
Protection against head injuries is important, as head trauma can lead to death or lifelong impairment. Falling objects, exposed beams, or electrical hazards can lead to potential injury, ad those working in situations where these elements are common should be outfitted with safety helmets to reduce injury risk. Hard hats, worn with the bill facing forward, should have a shock-absorbing lining and hard outer shell. The hats need to be water-resistant and slow to burn.
Foot and Leg Protection
Falling and rolling objects present a hazard to certain employees, as does corrosive or poisonous materials and hot substances. Non-conductive footwear that can resist piecing by falling sharp objects help protect the feet of employees, but leggings should also be added to protect the legs. Toe guards, shin guards, and metatarsal guards protect the toes and areas of the foot from compression hazards. Certain jobs may require specialty footwear, such as foundry shoes or electrically conductive shoes.
Hand and Arm Protection
Employees who may come into contact with chemicals or harmful substances could suffer burns or toxic skin absorption. Bruises, abrasions, fractures, punctures, and other injuries may occur without the right arm or hand protection. Protective gloves can be used to reduce the risk of skin contact with harmful substances, and there are several types of materials that can be used for glove construction. From leather to metal or liquid-resistant, the right glove depends on the working encounter.
Body Protection
It is likely that certain machine guards or work environments aren’t able to protect the employee’s body or torso from extreme temperatures, cast off of hot liquids or molten metals, equipment impact, or chemical contact. Protective clothing can be made to be disposable, such as paper-like fiber coverings, but they can also be made from leathers, rubber, plastics, treated cotton, or wool. The exposures faced on the job determine which clothing type is sufficient.
Hearing Protection
Exposure to loud noises, either temporarily or consistently while at work can lead to ear damage and hearing loss. Length of exposure and the loudness of the sound impact how often individuals should wear hearing protection, but the acceptable standard is exposure over 90 decibels for eight hours or longer each day requires appropriate ear protection. This could be earmuffs or various forms of earplugs.
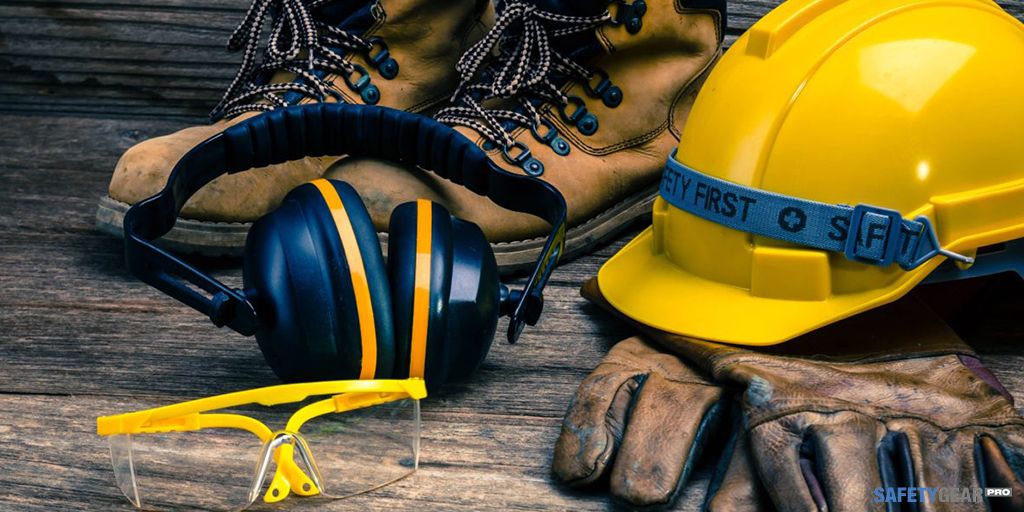

FAQs
How Do I Get My Protective Equipment?
If you are employed in an environment where OSHA regulations require protective equipment, your employer is required to distribute the appropriate forms of protection. Your employer may only provide the minimum safety gear, and you may want to invest in your own personal set of additional equipment to increase your level of protection.
What Happens If I Can’t Afford Safety Gear?
Fortunately, if federal guidelines for your job or industry mandate the use of safety gear, your employer is responsible for purchasing the equipment. They are not liable to pay for equipment that is supplemental. If at all possible, avoid buying used equipment as it may have wear and tear that reduces the protection offered.
How Do I Know If I Am Wearing the Right Safety Gear?
Your employer should provide adequate training in the use of the equipment required for your job. A workplace assessment is conducted, and in keeping with OSHA regulations, the appropriate forms of protection are established as hazards are identified. Hazards may first be addressed through equipment guards or safety mechanism, with personal equipment being secondary protection.
What Is the Most Important Safety Item?
Because of the various hazards associated with different jobs, there is no singular piece of equipment that is more important than the rest. Your job may require one or more types of protection as a first resort, while other pieces of equipment are a last resort. Follow your company’s guidelines for the use of all necessary items.
Am I Legally Required to Wear the Equipment?
Your employer is required to provide training and the equipment, and it is the employer’s responsibility to ensure that you are abiding by the rules and wearing your equipment. Failure to do so will result in workplace consequences rather than legal violations prosecuted in court. It is extremely important that you both know how to use your personal protective equipment and that you wear it when required. You are investing in your own health and safety. You can find a complete selection of high-quality protective clothing and accessories at Safety Gear Pro. You can choose from safety glasses to headgear, keeping your covered from head to toe.